The Ultimate Guide to Health Insurance Plans for U.S. Families (2025 Edition)
Meta Description:
Understand everything about health insurance in the United States. Compare plan types, learn how to lower premiums, and discover the best coverage for your family in 2025.
Keywords:
health insurance USA, best health insurance 2025, affordable family health insurance, medical insurance coverage, health insurance quotes US, health insurance for self-employed, health care plans America, private health insurance USA
Introduction
Health insurance in the United States is one of the most expensive—and most essential—types of coverage you can buy. Medical costs are rising every year, and one hospital visit can cost tens of thousands of dollars.
In 2025, the U.S. healthcare market is more complex than ever. Between government-backed plans, private insurers, employer coverage, and high-deductible options, understanding your choices is critical.
This guide will explain the key health insurance plan types, how premiums are calculated, and what steps you can take to get the best protection for your family at the most affordable price.

Why Health Insurance Matters
Without insurance, medical expenses can devastate your finances. A single emergency room visit in the U.S. can easily exceed $5,000.
Health insurance protects you from those catastrophic costs by sharing the risk across millions of people.
You pay a monthly premium, and your insurer helps pay for medical services—everything from routine checkups to surgeries and prescriptions.
For families, it’s not just about emergencies; it’s about preventive care, ensuring regular doctor visits, vaccines, and screenings are covered to keep everyone healthy.
The Main Types of Health Insurance Plans
1. Employer-Sponsored Insurance (ESI)
Most Americans get health coverage through their employers.
✅ Pros: Lower group rates, employer contributions, convenient payroll deductions.
❌ Cons: Limited provider networks; coverage ends if you change jobs.
2. Individual or Marketplace Plans
Purchased through HealthCare.gov or private marketplaces.
✅ Pros: Flexible, customizable options; subsidies available for low-income families.
❌ Cons: Can be expensive without tax credits.
3. Medicare
Government health insurance for people 65+ or with certain disabilities.
Includes Part A (hospital), Part B (medical), Part C (Advantage plans), and Part D (prescription drugs).
4. Medicaid
Free or low-cost coverage for low-income individuals and families. Eligibility depends on state income limits.
5. Short-Term and Catastrophic Plans
Designed for temporary gaps in coverage or young, healthy individuals.
⚠️ Warning: Often limited coverage and exclusions for preexisting conditions.
How Health Insurance Premiums Are Determined
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Older individuals pay more due to higher medical risk. |
| Location | Healthcare costs vary by state and even ZIP code. |
| Tobacco Use | Smokers may pay up to 50% higher premiums. |
| Plan Type | PPO and POS plans cost more than HMO. |
| Family Size | More dependents = higher premiums. |
| Income Level | Determines subsidy eligibility under ACA. |
💡 Pro Tip: Use the federal subsidy calculator on HealthCare.gov to see if you qualify for premium tax credits.

Understanding Plan Structures: HMO, PPO, EPO, POS
| Plan Type | Description | Cost Level | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) | Requires referrals and in-network doctors. | 💲💲 | Limited |
| PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) | No referrals; wider network. | 💲💲💲 | High |
| EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization) | In-network only but no referrals needed. | 💲💲 | Medium |
| POS (Point of Service) | Combines HMO + PPO features. | 💲💲💲 | Medium-High |
If your family prefers flexibility and travels often, PPO or POS plans might fit best.
If you want lower costs and don’t mind limited doctors, HMO works well.
Key Health Insurance Terms You Must Know
-
Premium: The monthly payment you make to keep your insurance active.
-
Deductible: The amount you pay out-of-pocket before your insurer starts paying.
-
Co-pay: A fixed fee you pay for each doctor visit or prescription.
-
Co-insurance: The percentage you pay after meeting your deductible (e.g., 20%).
-
Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The most you’ll pay per year—after that, insurance covers 100%.
Understanding these terms helps you calculate your true total annual cost, not just the monthly premium.
Best Health Insurance Companies in the U.S. (2025)
| Company | Best For | Average Monthly Premium |
|---|---|---|
| Blue Cross Blue Shield | Nationwide network & trusted reputation | $480 |
| UnitedHealthcare | Strong digital tools & telehealth services | $510 |
| Kaiser Permanente | Top-rated customer satisfaction | $465 |
| Aetna | Affordable plans for individuals & families | $440 |
| Cigna | Great for international coverage | $490 |
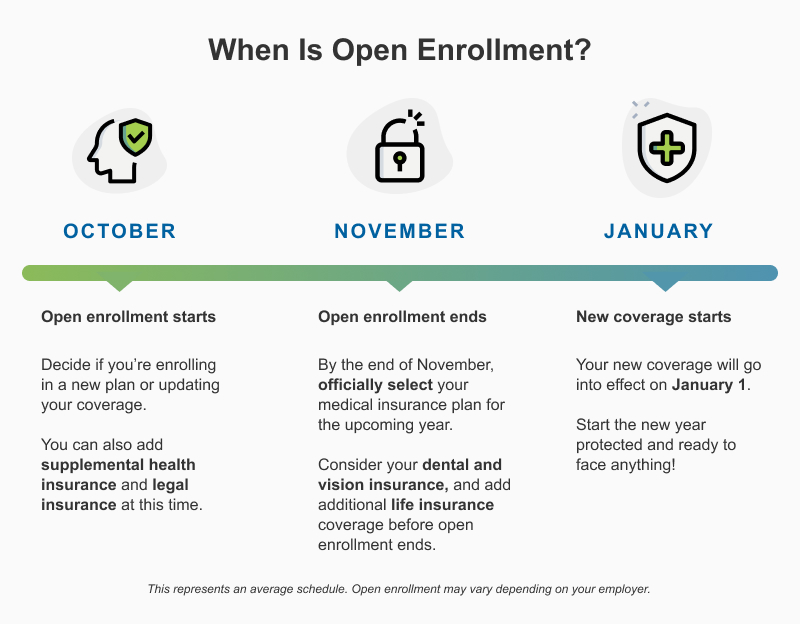
Tips to Save Money on Health Insurance in 2025
-
Shop During Open Enrollment: Compare plans every year (November–January).
-
Use Preventive Care: Annual checkups and vaccines are free under ACA-compliant plans.
-
Check Subsidy Eligibility: Families earning under $90,000 may qualify for discounts.
-
Consider High-Deductible Plans (HDHP): Pair them with a Health Savings Account (HSA) for tax-free savings.
-
Use Telehealth: Virtual visits are cheaper and often covered.
-
Stay In-Network: Out-of-network visits can double your bill.
Common Health Insurance Mistakes to Avoid
-
Ignoring the deductible and focusing only on monthly cost.
-
Choosing a plan with a small provider network.
-
Forgetting to report income changes to the Marketplace.
-
Letting your coverage lapse—medical debt can ruin credit.
The Future of Health Insurance in America
The 2025 U.S. healthcare landscape is rapidly evolving:
-
AI-driven claims processing reduces fraud and speeds approvals.
-
Wearable health data (Fitbit, Apple Watch) influences wellness discounts.
-
Expanded telemedicine gives access to rural areas.
-
Employer hybrid plans allow flexible contribution models.
Experts predict that health insurance will continue to blend traditional coverage with digital health ecosystems, giving families more personalized, affordable options.
Conclusion
Health insurance is no longer optional—it’s financial survival.
By understanding how plans work, comparing different structures, and exploring subsidies, you can protect your family without overpaying.
Your health is your most valuable asset.
Invest in it wisely—review your plan each year, know your benefits, and use preventive care to stay ahead.
